 |
 |
| Tuberc Respir Dis > Volume 87(1); 2024 > Article |
|
Abstract
Notes
AuthorsŌĆÖ Contributions
Conceptualization: Hong SH. Writing - original draft preparation: Jung JH, Yang SR, Kim WJ, Rhee CK. Writing - review and editing: Hong SH. Approval of final manuscript: all authors.
Funding
This research was supported by a grant from the Korean Fund for Regenerative Medicine (KFRM) funded by the Korean government (the Ministry of Science and ICT, the Ministry of Health & Welfare) (22A0304L1-01) as well as the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation (NRF) funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (2022M3A9E4016936). Finally, this study was funded in part by Particulate Matter Management Specialized Graduate Program through the Korea Environmental Industry & Technology Institute (KEITI) and the KEITI through the Core Technology Development Project for Environmental Disease Prevention and Management (Grant number 2022003310008) funded by the Ministry of Environment (MOE).
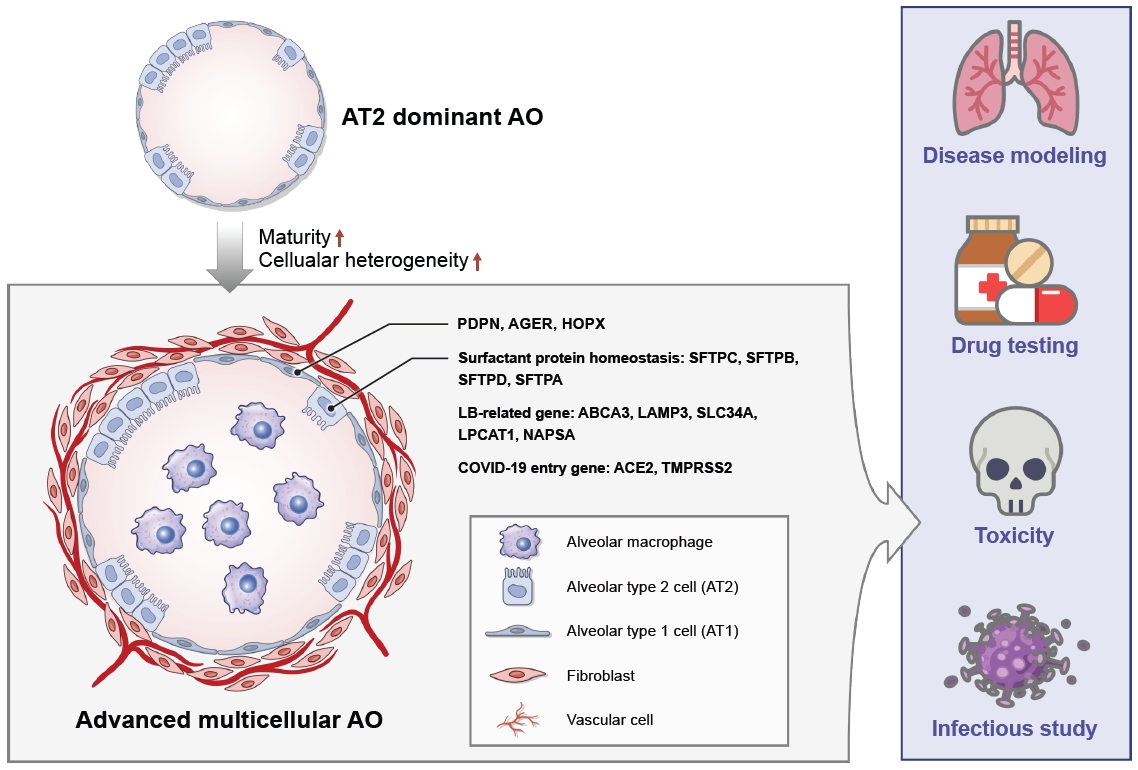
Figure┬Ā1.

Table┬Ā1.
| Application | Significant findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| PF modeling | ||
| ŌĆāBLM treatment | BLM treatment (10 ╬╝g/mL) for 48 hours | [37,38,45] |
| Higher fibroblast proliferation and larger fibrotic area in the BLM-treated AOs | ||
| Upregulation of fibrosis-related marker expression: ╬▒-SMA , ICAM-1 , IL-1╬▓ , IL-6 , FN , and TGF-╬▓1 | ||
| CDKN1A, an indicator of DNA damage up-regulated in a BLM concentration-dependent manner | ||
| ŌĆāTGF-╬▓1 treatment | Treatment of TGF-╬▓1 (25 ng/mL) for 72 hours | [40,49] |
| ECM (COL1A1 and COL1A2), mesenchymal cells (VIMENTIN) and FMT (╬▒-SMA , CTNNB1 , TWIST1 , and SNAIL1)-related genes were increased | ||
| Collagen, fibronectin, ERK, and SMAD2/3 proteins were activated | ||
| Alleviation of fibrotic changes by treatment of potential drug (NP011) and two FDA-approved drugs (Nintedanib and Pirfenidone) | ||
| Infection study | ||
| ŌĆāSARS-CoV-2 | Viral particles were observed in the apical, lateral and basolateral side of the organoids | [46,47] |
| Enveloped viruses were observed in the lumen of Golgi apparatus and secretory vesicles | ||
| Upregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, NF-╬║B-related genes, and interferon-stimulated genes, which are consistent with previous observations in lung tissues of COVID-19 patients | ||
| Tested the inhibitory effect of a neutralizing antibody CB6 on virus infection | ||
| CB6 significantly repressed the production of infectious viral particles | ||
| Toxicity | ||
| ŌĆāPM2.5 | Upregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and entry receptor (AEC2 and TMPRSS2) of SARS-CoV-2 by treatment with dPM2.5 | [41] |
| Exposure to dPM2.5 markedly increased the transcript levels of the mesenchymal markers | ||
| dPM2.5-induced cellular and molecular alterations such as EMT and oxidative stress | ||
| SFTPC expression was not affected by treatment of dPM2.5 | ||
| ŌĆāToxic chemicals: classified as "acute toxicity, inhalation" hazard | Cell viability was significantly decreased in a dose-dependent manner of chemicals; chromium (VI) trioxide, sodium chromate, potassium dichromate, chloroacetic acid, glycolic acid, ethephon, guanidine monohydrochloride, sodium nitrite, and o-phenylenediamine | [42] |
AO: alveolar organoid; PF: pulmonary fibrosis; BLM: bleomycin; ╬▒-SMA: ╬▒-smooth muscle actin; ICAM-1 : intercellular adhesion molecule 1; IL : interleukin; FN : fibronectin; TGF-╬▓1: transforming growth factor-╬▓1; CDKN1A : cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 1A; ECM: extracellular matrix; COL1A1 : collagen type I alpha 1 chain; COL1A2 : collagen type I alpha 2 chain; FMT: fibroblast to myofibroblast transition; CTNNB1 : catenin beta 1; TWIST1 : twist-related protein 1; SNAIL1 : snail family transcriptional repressor 1; ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinase; SMAD2/3: suppressor mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 2/3; FDA: U.S. Food and Drug Administration; SARS-CoV-2: severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; NF-╬║B: nuclear factor-╬║B; COVID-19: coronavirus disease 2019; PM2.5: particulate matter 2.5; AEC2: alveolar epithelial cell 2; TMPRSS2: transmembrane serine protease 2; dPM2.5: diesel fine PM2.5; EMT: epithelial to mesenchymal transition; SFTPC: surfactant-associated protein C.
REFERENCES
-
METRICS

-
- 0 Crossref
- 0 Scopus
- 1,313 View
- 158 Download
- ORCID iDs
-
Ji-hye Jung

https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1638-8823Seok-Ho Hong

https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3372-442X - Funding Information
-
Korean Fund for Regenerative Medicine
Ministry of Science and ICT
Ministry of Health and Welfare
https://doi.org/10.13039/501100003625
22A0304L1-01National Research Foundation of Korea
https://doi.org/10.13039/501100003725
2022M3A9E 4016936Korea Environmental Industry and Technology Insitute
https://doi.org/10.13039/501100003654Ministry of Environment
https://doi.org/10.13039/501100003562
2022003310008 - Related articles


 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Print
Print Download Citation
Download Citation



