 |
 |
| Tuberc Respir Dis > Volume 85(4); 2022 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background
Methods
Results
Notes
Authors’ Contributions
Conceptualization: Sim JK, Lee YS. Methodology: Lee YS. Validation: Min KH, Hur GY, Lee SY, Shim JJ. Formal analysis: Sim JK. Data curation: Sim JK, Choi J, Oh JY. Writing - original draft preparation: Sim JK. Writing - review and editing: Sim JK, Lee YS. Approval of final manuscript: all authors.
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Figure S1.
Figure 1.
Figure 2.
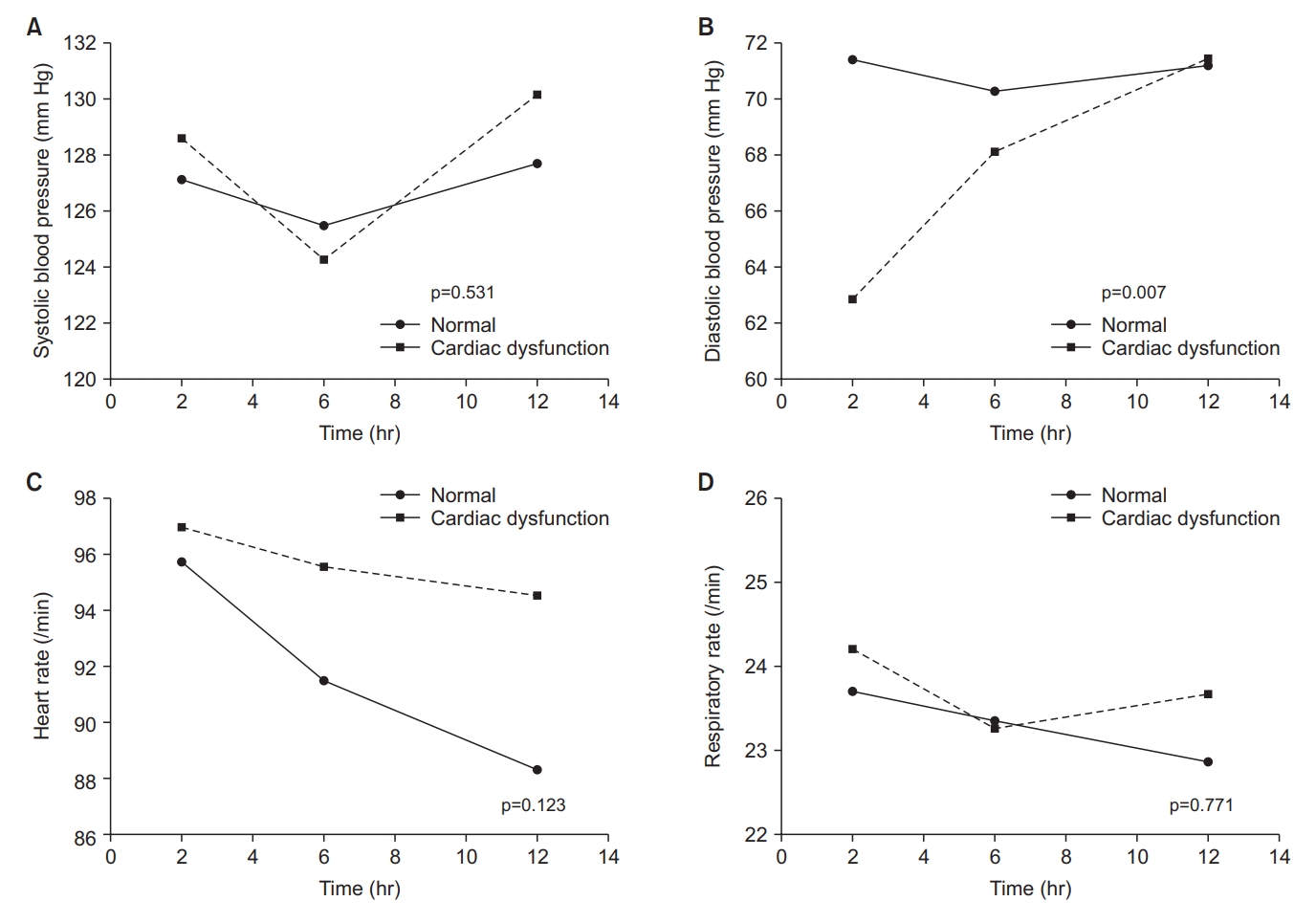
Figure 3.
Figure 4.
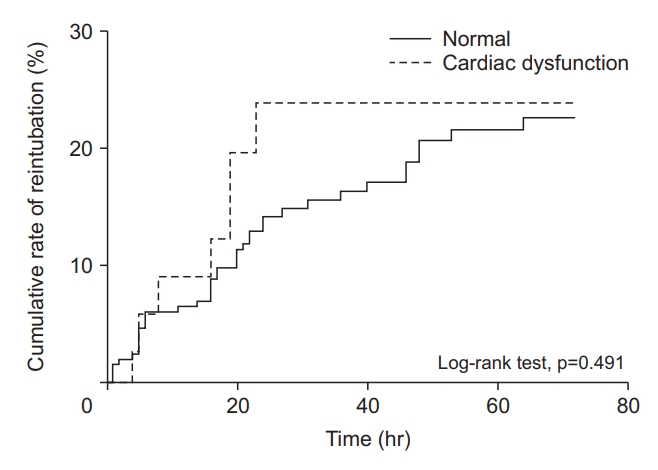
Table 1.
| Variable | Normal (n=235) | Cardiac dysfunction (n=35) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 149 (63.4) | 22 (62.9) | >0.99 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 21 (18-24) | 22 (20-26) | 0.110 |
| APACHE II | 30 (27-33) | 31 (28-34) | 0.119 |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index | 6 (4-8) | 6 (4-8) | 0.185 |
| Admission diagnosis | |||
| Cardiac disease | 11 (4.7) | 1 (2.9) | >0.99 |
| Pulmonary disease | 146 (62.1) | 26 (74.3) | 0.190 |
| Gastrointestinal disease | 4 (1.7) | 0 (0) | >0.99 |
| Renal disease | 2 (0.9) | 0 (0) | >0.99 |
| Neurologic disease | 20 (8.5) | 2 (5.7) | 0.749 |
| Malignancy | 2 (0.9) | 0 (0) | >0.99 |
| Others | 50 (21.3) | 6 (17.1) | 0.661 |
| Cause of respiratory failure* | |||
| Pulmonary | 209 (89.3) | 32 (91.4) | 0.833 |
| Extra-pulmonary | 25 (10.7) | 3 (8.6) | >0.99 |
| Blood gas analysis† | |||
| pH | 7.49 (7.45-7.52) | 7.48 (7.45-7.52) | 0.682 |
| PaCO2, mm Hg | 35 (31-40) | 35 (31-37) | 0.308 |
| PaO2, mm Hg | 103 (81-126) | 121 (92-135) | 0.009 |
| HCO3, mmol/L | 27 (23-30) | 26 (23-28) | 0.132 |
| SaO2, % | 98 (97-99) | 99 (98-99) | 0.076 |
| PaO2/FiO2 ratio† | 286 (223-390) | 373 (290-437) | 0.001 |
| Vital signs† | |||
| SBP, mm Hg | 129 (113-144) | 124 (112-142) | 0.539 |
| DBP, mm Hg | 71 (61-81) | 66 (58-80) | 0.141 |
| HR, /min | 93 (80-106) | 92 (84-107) | 0.987 |
| RR, /min | 21 (17-26) | 20 (17-25) | 0.361 |
| Vasoactive agent use† | 84 (35.7) | 23 (65.7) | 0.001 |
| Norepinephrine | 55 (23.4) | 12 (34.3) | 0.207 |
| Dopamine | 10 (4.3) | 3 (8.6) | 0.229 |
| Dobutamine | 38 (16.2) | 16 (45.7) | <0.001 |
| Renal replacement therapy† | 22 (9.4) | 7 (20.0) | 0.076 |
| SOFA score† | 7 (5-9) | 7 (5-10) | 0.394 |
Values are presented as median (interquartile range) or number (%).
Patients were divided into normal function group (ejection fraction ≥45%) and cardiac dysfunction group (ejection fraction <45%).
BMI: body mass index; APACHE II: Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II; PaCO2: partial pressure of carbon dioxide; PaO2: partial pressure of oxygen; SaO2: arterial oxygen saturation; FiO2: fraction of inspired oxygen; SBP: systolic blood pressure; DBP: diastolic blood pressure; HR: heart rate; RR: respiratory rate; SOFA: Sequential Organ Failure Assessment.
Table 2.
Table 3.
Multivariate Cox regression analysis was performed to investigate factors affecting the reintubation within 72 hours after extubation incorporating cardiac dysfunction and other variables with p-value less than 0.05 in univariate analysis.
HR: hazard ratio; CI: confidence interval; EF: ejection fraction; APACHE II: Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II; SOFA: Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; PaO2/FiO2 ratio: partial pressure of oxygen and fraction of inspired oxygen ratio; PaCO2: partial pressure of carbon dioxide.
References
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

- ORCID iDs
-
Jae Kyeom Sim

https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0873-2807Young Seok Lee

https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0144-2033 - Related articles


 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Data Sharing Statement
Data Sharing Statement Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Supplement1
Supplement1 Print
Print Download Citation
Download Citation



